To prevent dehydration of the client the nurse aide should – To prevent dehydration of the client, the nurse aide plays a crucial role in monitoring, assessing, and managing fluid intake. This article explores the importance of hydration, methods for assessing hydration status, and strategies for preventing dehydration in clients.
Patient Monitoring and Assessment: To Prevent Dehydration Of The Client The Nurse Aide Should
Monitoring the client’s hydration status is essential to prevent dehydration. This involves assessing the client’s fluid intake and output, as well as monitoring for signs and symptoms of dehydration.
Methods for Assessing Hydration Status
* Monitoring fluid intake and output
- Assessing skin turgor
- Checking mucous membranes
- Measuring urine output
- Observing for signs of dehydration
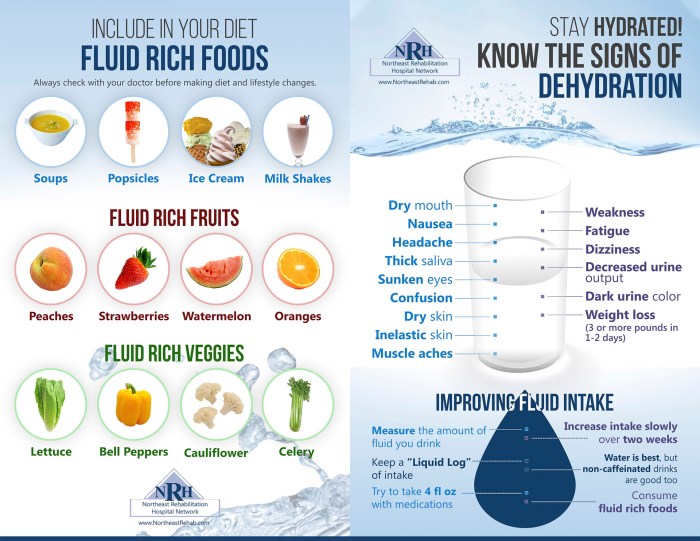
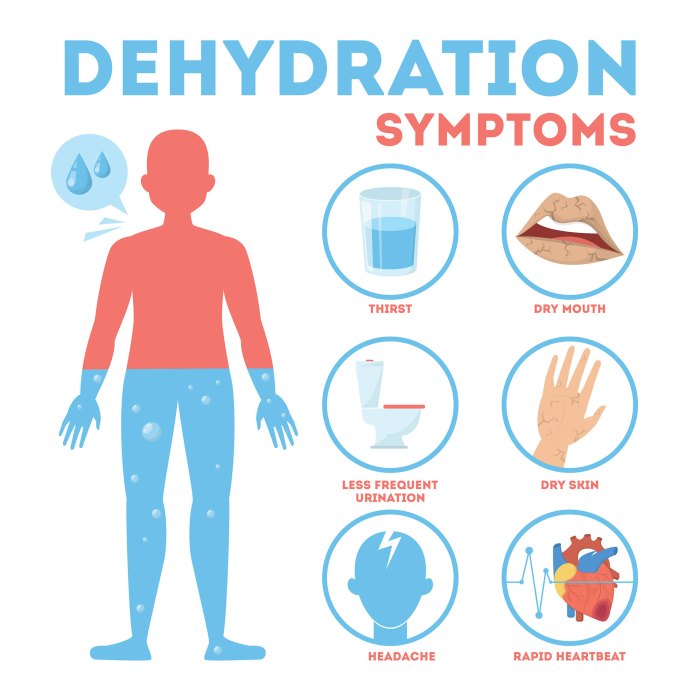
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
* Dry mouth
- Thirst
- Sunken eyes
- Decreased urine output
- Dark urine
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Rapid heart rate
- Low blood pressure
Fluid Intake Management
The recommended daily fluid intake for adults is eight glasses of water per day. However, this amount may vary depending on factors such as activity level, climate, and health conditions.
Importance of Offering Fluids Frequently
Offering fluids frequently helps to prevent dehydration by ensuring that the client is consuming fluids throughout the day.
Methods for Encouraging Fluid Intake
* Providing a variety of fluids, such as water, juice, and soup
- Offering fluids in a variety of ways, such as in a cup, bottle, or straw
- Making fluids easily accessible by placing them within reach of the client
Oral Hydration
Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are used to treat dehydration by replacing lost fluids and electrolytes. ORS can be prepared at home using a recipe from the World Health Organization (WHO).
Benefits of Oral Rehydration Solutions
* Replaces lost fluids and electrolytes
- Prevents dehydration
- Can be administered easily and quickly
Importance of Administering Oral Fluids Slowly and in Small Amounts
Administering oral fluids slowly and in small amounts helps to prevent nausea and vomiting.
Intravenous Fluid Therapy
Intravenous fluid therapy (IVT) is used to treat severe dehydration when oral rehydration is not possible. IVT involves administering fluids directly into a vein.
Indications for Intravenous Fluid Therapy
* Severe dehydration
- Inability to tolerate oral fluids
- Loss of consciousness
Types of Intravenous Fluids Used to Prevent Dehydration
* Isotonic fluids
- Hypotonic fluids
- Hypertonic fluids
Administration of Intravenous Fluids
IVT is administered using a sterile technique and aseptic precautions. The rate of fluid administration is determined by the client’s condition and fluid requirements.
Dietary Modifications
Consuming foods and beverages that are high in water content can help to prevent dehydration.
Foods and Beverages High in Water Content, To prevent dehydration of the client the nurse aide should
* Fruits and vegetables
- Soups and broths
- Dairy products
- Sports drinks
Importance of Avoiding Foods and Beverages that Can Worsen Dehydration
Certain foods and beverages can worsen dehydration, such as:* Salty foods
- Sugary drinks
- Alcohol
Role of Electrolytes in Hydration
Electrolytes are minerals that help to regulate fluid balance in the body. Consuming foods and beverages that are rich in electrolytes can help to prevent dehydration.
Environmental Factors
Heat and humidity can increase the risk of dehydration.
Effects of Heat and Humidity on Hydration
* Heat causes the body to sweat, which can lead to fluid loss.
Humidity reduces the evaporation of sweat, which can make it difficult to cool down and can lead to dehydration.
Measures to Prevent Dehydration in Hot and Humid Environments
* Stay in cool and shaded areas
- Wear loose-fitting clothing
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Take cool showers or baths
Tips for Maintaining a Cool and Comfortable Environment for the Client
* Use air conditioning or fans
- Open windows and doors to allow for ventilation
- Provide cool drinks and ice packs
Education and Support
Educating the client and their family about how to prevent dehydration is essential.
Tips on How to Prevent Dehydration at Home
* Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day
- Eat foods that are high in water content
- Avoid foods and beverages that can worsen dehydration
- Stay cool and hydrated in hot and humid environments
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention if Signs of Dehydration are Present
If signs of dehydration are present, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Role of the Nurse Aide in Supporting the Client’s Hydration Needs
The nurse aide plays a vital role in supporting the client’s hydration needs by:* Monitoring the client’s fluid intake and output
- Assessing the client for signs and symptoms of dehydration
- Encouraging the client to drink fluids
- Assisting with oral rehydration therapy
- Administering intravenous fluids as prescribed
- Educating the client and their family about how to prevent dehydration
FAQ Overview
What are the signs and symptoms of dehydration?
Signs and symptoms of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, decreased urine output, fatigue, and dizziness.
How can I prevent dehydration in hot and humid environments?
To prevent dehydration in hot and humid environments, it is important to drink plenty of fluids, avoid excessive physical activity, and stay in cool and air-conditioned areas.
What role does the nurse aide play in supporting the client’s hydration needs?
The nurse aide plays a crucial role in supporting the client’s hydration needs by monitoring fluid intake, assessing hydration status, and providing assistance with oral or intravenous fluids as needed.