Eustachian tube frog function and location – The Eustachian tube, a crucial component of the auditory system in frogs, warrants exploration. This intricate structure, connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, plays a pivotal role in hearing and maintaining pressure equilibrium. Its anatomy, functions, and implications for overall health necessitate a comprehensive examination.
In this discourse, we delve into the intricacies of the Eustachian tube in frogs, deciphering its structure, functions, and potential dysfunctions. Furthermore, we provide practical guidance for maintaining Eustachian tube health and explore treatment options for any impairments.
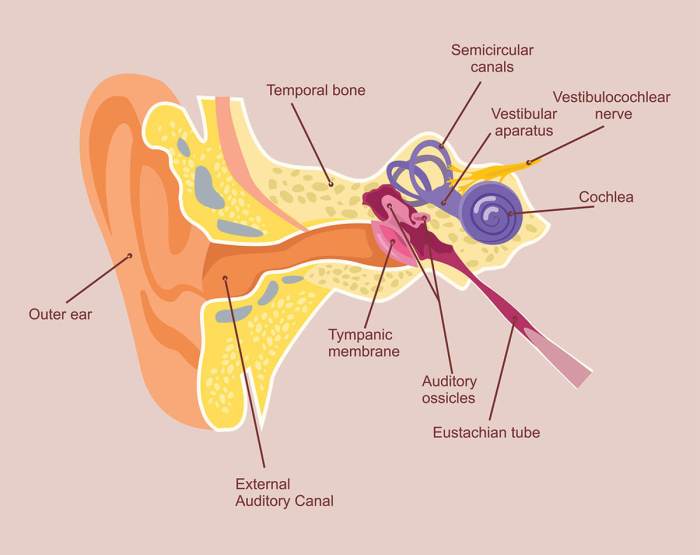
Eustachian Tube Anatomy
The Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube, is a vital part of the human auditory system. It plays a crucial role in hearing and maintaining the health of the middle ear.
Location
The Eustachian tube is a narrow, muscular channel that connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat behind the nose). It runs through the temporal bone of the skull and opens into the middle ear cavity on one end and the nasopharynx on the other.
Structure
The Eustachian tube consists of two main sections:
- Cartilaginous portion:The outer third of the tube is made of cartilage and is fixed to the temporal bone.
- Membranous portion:The inner two-thirds of the tube is made of a thin, membranous lining and is supported by muscles.
The muscles surrounding the Eustachian tube help to open and close it, regulating the flow of air and mucus through the tube.
Diagram
[Masukan ilustrasi diagram Eustachian tube di sini]
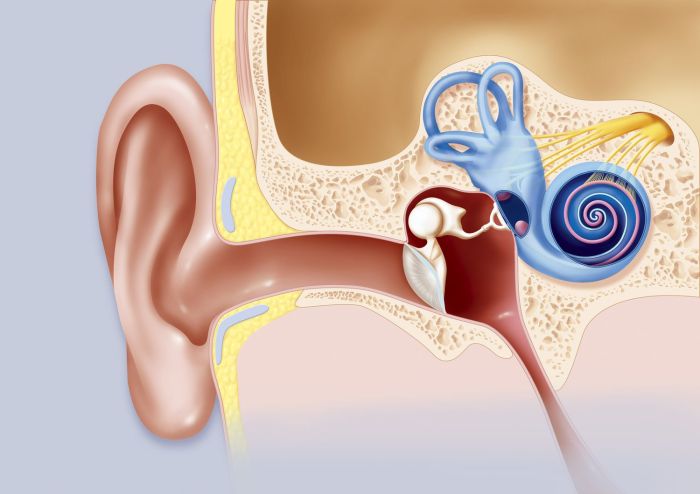
Eustachian Tube Function
The Eustachian tube plays several important roles in hearing and middle ear health:
Hearing
The Eustachian tube helps to equalize air pressure between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. This is essential for proper sound transmission. When the air pressure in the middle ear is lower than the pressure in the nasopharynx, the Eustachian tube opens to allow air to enter the middle ear, restoring the balance.
Opening and Closing
The Eustachian tube is normally closed, except during swallowing, yawning, or other activities that increase the pressure in the nasopharynx. When the pressure increases, the muscles surrounding the tube contract, pulling the tube open and allowing air to flow through.
Regulation of Pressure
By regulating the air pressure in the middle ear, the Eustachian tube helps to protect the delicate structures of the inner ear from damage. It also helps to drain mucus from the middle ear, preventing the buildup of fluid and potential infections.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the tube is unable to function properly, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health issues.
Causes
Eustachian tube dysfunction can be caused by various factors, including:
- Allergies
- Infections (e.g., colds, flu)
- Sinusitis
- Smoking
- Nasal polyps
- Enlarged adenoids
Symptoms, Eustachian tube frog function and location
Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction may include:
- Ear pain
- Ear fullness
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Popping or clicking sounds in the ears
Impact
Eustachian tube dysfunction can significantly impact hearing and overall health. Untreated, it can lead to chronic ear infections, hearing loss, and even damage to the inner ear.
Eustachian Tube Management
Maintaining Eustachian tube health is crucial for optimal hearing and overall well-being. Here are some tips:
Tips for Health
- Avoid smoking.
- Control allergies and sinus infections.
- Use nasal sprays or decongestants to reduce nasal congestion.
- Chew gum or suck on hard candies to stimulate saliva production, which helps to keep the Eustachian tube open.
- Practice the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing into the nose while pinching it closed) to equalize pressure in the ears.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction depends on the underlying cause. It may include:
- Antibiotics (for infections)
- Nasal corticosteroids (for allergies and sinusitis)
- Surgery (in severe cases, such as with enlarged adenoids or nasal polyps)
Importance of Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment of Eustachian tube dysfunction is crucial to prevent complications and preserve hearing. If you experience persistent ear pain, fullness, or hearing loss, consult with a healthcare professional promptly.
Frequently Asked Questions: Eustachian Tube Frog Function And Location
What is the primary function of the Eustachian tube in frogs?
The Eustachian tube’s primary function is to facilitate hearing by transmitting sound vibrations from the middle ear to the inner ear.
How does the Eustachian tube regulate pressure in frogs?
The Eustachian tube helps regulate pressure between the middle ear and the nasopharynx, ensuring optimal sound transmission and protecting the delicate structures of the inner ear.
What are the potential causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction in frogs?
Eustachian tube dysfunction in frogs can result from various factors, including infections, allergies, and structural abnormalities.
How can I prevent Eustachian tube issues in my frog?
Maintaining a clean and healthy environment, avoiding exposure to irritants, and ensuring proper hydration can help prevent Eustachian tube issues in frogs.