Unveiling the profound impact of drug use on the brain, “How Do Drugs Affect the Brain Brainly” delves into the intricate neurobiology of addiction, cognitive and behavioral alterations, and the multifaceted consequences of substance abuse. This exploration illuminates the complex interplay between drugs and the human brain, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical societal issue.
The ensuing paragraphs dissect the mechanisms by which drugs hijack the brain’s reward system, altering neurotransmitter activity and inducing tolerance and dependence. We examine the cognitive impairments associated with drug use, including memory deficits, impaired attention, and compromised decision-making. Moreover, we explore the behavioral changes that accompany addiction, such as aggression, impulsivity, and social withdrawal.
Introduction: How Do Drugs Affect The Brain Brainly
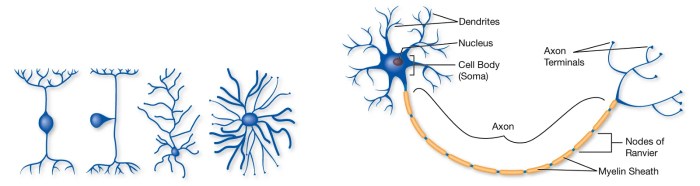
Understanding the impact of drugs on the brain is crucial due to the prevalence of drug use and its significant societal consequences. Drugs can alter brain chemistry, leading to a range of cognitive, behavioral, and physical effects.
Neurobiology of Drug Addiction
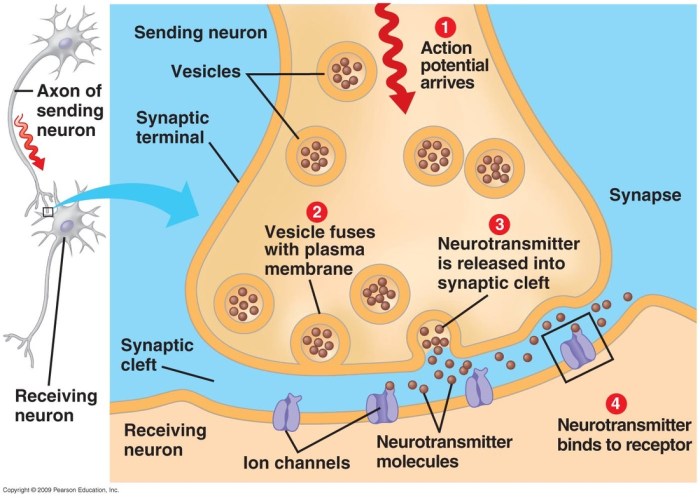
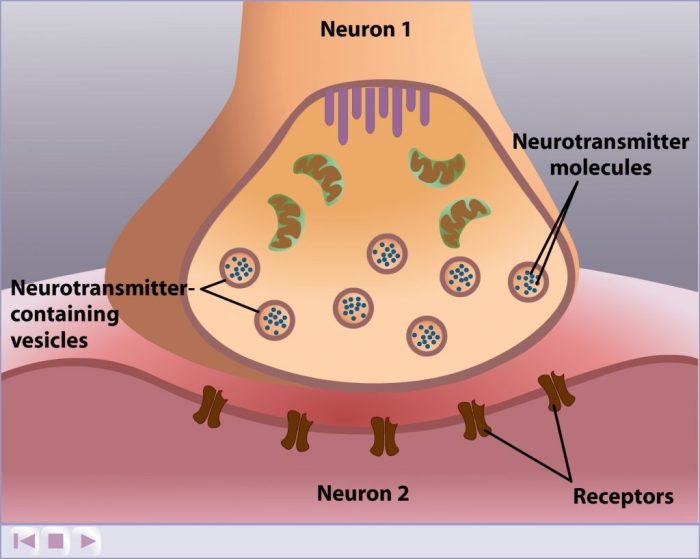
The brain’s reward system plays a key role in drug addiction. Drugs interact with neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, to activate this system, leading to feelings of pleasure and reinforcement. Repeated drug use can lead to tolerance and dependence, as the brain adapts to the presence of the drug.
Cognitive and Behavioral Effects of Drugs
- Drugs can impair cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and decision-making.
- Behavioral changes associated with drug use include aggression, impulsivity, and social isolation.
- Specific drugs, such as marijuana, can impair short-term memory, while cocaine can increase impulsivity.
Physical and Health Consequences of Drug Use, How do drugs affect the brain brainly
- Short-term effects include respiratory depression, seizures, and cardiovascular problems.
- Long-term effects include organ damage, malnutrition, and infectious diseases.
- Drug use can contribute to mental health disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis.
Treatment and Prevention
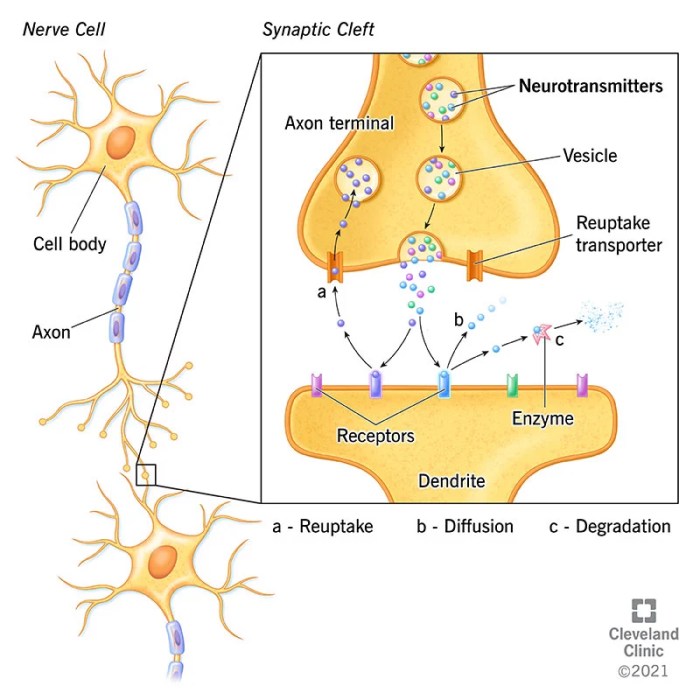
Treatment options for drug addiction include therapy, medication, and support groups. Prevention programs aim to reduce drug use and its consequences through education, outreach, and policy initiatives.
Key Questions Answered
What are the common neurotransmitters affected by drugs?
Dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate are among the neurotransmitters commonly targeted by drugs.
How does drug use contribute to mental health disorders?
Drug use can exacerbate or trigger mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis.
What are the long-term physical consequences of drug use?
Long-term drug use can lead to organ damage, malnutrition, infectious diseases, and increased risk of chronic health conditions.