Privacy by design lex course answers – Delving into the intricacies of privacy by design, this course provides a comprehensive exploration of the foundational principles, legal frameworks, practical applications, and future trends shaping this critical field. Our meticulously crafted answers empower you to navigate the complexities of privacy protection and data security, ensuring compliance and safeguarding the rights of individuals in the digital age.
Privacy by Design Principles: Privacy By Design Lex Course Answers
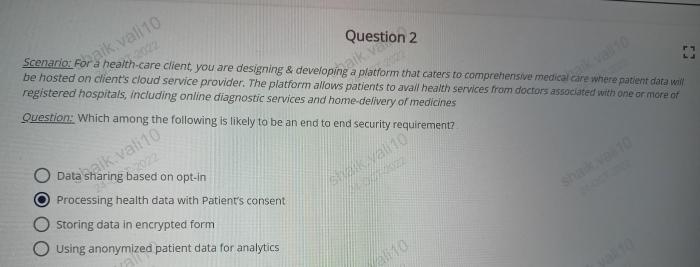
Privacy by design is a proactive approach to data protection that aims to embed privacy considerations into the design and development of systems and technologies. This approach seeks to minimize the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data, while also providing individuals with control over their personal information.
The seven foundational principles of privacy by design are:
- Proactive not reactive:Privacy should be considered from the outset of any system or technology development, not as an afterthought.
- Privacy as the default setting:Systems and technologies should be designed to protect privacy by default, without requiring users to take additional steps.
- Privacy embedded into design:Privacy considerations should be integrated into all aspects of system and technology design, including data collection, storage, use, and disclosure.
- Full lifecycle protection:Privacy protections should be maintained throughout the entire lifecycle of a system or technology, from design and development to deployment and maintenance.
- Respect for user privacy:Systems and technologies should be designed to respect the privacy rights of individuals, including the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data.
- Accountability:Organizations should be accountable for the privacy of the personal data they collect and process.
li> Visibility and transparency:Individuals should be able to easily understand how their personal data is being collected, used, and disclosed.
Implementing privacy by design principles can help organizations to:
- Reduce the risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
- Build trust with customers and stakeholders.
- Comply with privacy regulations.
- Gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
However, adopting privacy by design practices can also present some challenges, such as:
- Increased costs:Implementing privacy by design measures can require additional time and resources.
- Complexity:Privacy by design can be complex to implement, especially in large and complex systems.
- Lack of expertise:Many organizations lack the necessary expertise to implement privacy by design effectively.
Despite these challenges, privacy by design is an essential approach for organizations that want to protect the privacy of their customers and stakeholders. By embedding privacy considerations into the design and development of their systems and technologies, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and privacy violations, build trust, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of Privacy by Design
Privacy by Design is a proactive approach to privacy protection that embeds privacy considerations into the design and implementation of technologies, systems, and business practices. It is guided by several legal and regulatory frameworks that establish the obligations and responsibilities of organizations in protecting personal data.
These frameworks include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) of Canada
These frameworks impose specific requirements on organizations, such as:
- Obtaining informed consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal data
- Providing individuals with access to their personal data and the right to rectify or erase it
- Implementing appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure
Privacy by Design principles help organizations comply with these legal and regulatory requirements by:
- Minimizing the collection and processing of personal data
- Using anonymization and pseudonymization techniques to protect personal data
- Implementing privacy-enhancing technologies, such as encryption and access control
Privacy Impact Assessments
Privacy impact assessments (PIAs) are a key tool for ensuring compliance with privacy regulations. PIAs help organizations identify and mitigate privacy risks associated with the design and implementation of new technologies or business practices. They involve:
- Identifying the personal data that will be collected and processed
- Assessing the potential privacy risks associated with the processing
- Developing mitigation strategies to address the risks
PIAs are an essential part of the Privacy by Design process and help organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting personal data.
Privacy by Design in Practice

Privacy by design (PbD) is a proactive approach to privacy that seeks to embed privacy considerations into the design of systems and technologies from the outset. This approach can help to mitigate privacy risks and protect individuals’ personal information.
There are a number of successful examples of PbD implementations in various industries. For example, the following case studies highlight some of the key factors that have contributed to the success of these implementations:
Case Study 1
Company:Google
Product:Android operating system
Key factors:
- Google has implemented a number of PbD features into Android, such as:
- The ability to control app permissions
- The use of data minimization techniques
- The provision of clear and concise privacy policies
- These features have helped to make Android one of the most privacy-friendly mobile operating systems on the market.
Case Study 2
Company:Apple
Product:iOS operating system
Key factors:
- Apple has also implemented a number of PbD features into iOS, such as:
- The use of strong encryption
- The ability to restrict data sharing
- The provision of privacy-focused features, such as Face ID and Touch ID
- These features have helped to make iOS one of the most privacy-friendly mobile operating systems on the market.
Case Study 3, Privacy by design lex course answers
Company:Microsoft
Product:Windows 10 operating system
Key factors:
- Microsoft has implemented a number of PbD features into Windows 10, such as:
- The ability to control data collection and sharing
- The use of privacy-enhancing technologies, such as Differential Privacy
- The provision of clear and concise privacy policies
- These features have helped to make Windows 10 a more privacy-friendly operating system.
These case studies demonstrate that PbD can be successfully implemented in a variety of industries. By incorporating PbD principles into the design of their products and services, companies can help to protect individuals’ privacy and build trust with their customers.
Future Trends in Privacy by Design
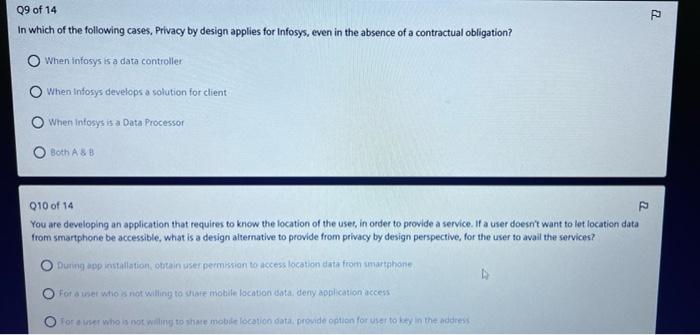
The future of privacy by design is shaped by emerging technologies and trends that have significant implications for data protection and privacy. These include advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain technology, among others. Understanding these trends and their potential impact is crucial for advancing privacy by design practices.
AI and Privacy by Design
- AI algorithms can process vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy and algorithmic bias. Privacy by design approaches can help ensure that AI systems are developed with privacy protections in place, such as data minimization, transparency, and user control.
- AI can also be used to enhance privacy by automating privacy-enhancing technologies, such as anonymization and encryption.
IoT and Privacy by Design
- IoT devices collect and transmit vast amounts of data, creating new privacy risks. Privacy by design principles can guide the development of IoT devices and systems to minimize data collection, protect data in transit and storage, and provide users with control over their data.
- Privacy-enhancing technologies, such as secure data transmission protocols and access control mechanisms, can be incorporated into IoT devices to protect user privacy.
Blockchain and Privacy by Design
- Blockchain technology offers potential for enhancing privacy by providing secure and transparent data storage and sharing. Privacy by design principles can help ensure that blockchain-based systems are developed with privacy protections, such as data minimization, access control, and user consent.
- Blockchain can also be used to develop privacy-enhancing tools, such as anonymous credentials and privacy-preserving smart contracts.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key principles of privacy by design?
Privacy by design encompasses seven foundational principles: data minimization, purpose limitation, data retention, transparency, user control, integrity, and security.
How does privacy by design impact legal compliance?
Privacy by design aligns with various legal frameworks, including the GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
What are the benefits of implementing privacy by design?
Privacy by design enhances trust, reduces data breaches, improves customer satisfaction, and fosters innovation by creating a secure foundation for data processing.