Welcome to the realm of DNA profiling, where the dna profiling gizmo answer key unlocks the mysteries of genetics. Delve into the captivating world of DNA analysis, unraveling the intricate tapestry of our genetic heritage.
This comprehensive guide will illuminate the process of DNA profiling, empowering you with the knowledge to interpret DNA patterns and uncover hidden truths.
DNA Profiling
DNA profiling is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA patterns. It is commonly used in forensic science, paternity testing, and medical research.
The process of DNA profiling involves collecting a sample of DNA from an individual, such as blood, saliva, or hair. The DNA is then extracted and analyzed to identify specific genetic markers, known as alleles. These alleles are inherited from both parents and are unique to each individual, except in the case of identical twins.
Sample Collection
DNA samples can be collected from various sources, including blood, saliva, hair, and tissue. The collection method depends on the availability and condition of the sample.
- Blood:Blood is the most common source of DNA for profiling. It is collected through a simple blood draw.
- Saliva:Saliva can be collected using a swab or a saliva collection kit. It is a non-invasive method that is often used for paternity testing.
- Hair:Hair samples can be collected from the root or the shaft. Hair samples are often used in forensic investigations.
- Tissue:Tissue samples can be collected from various parts of the body, such as skin, muscle, or bone. Tissue samples are often used in medical research.
DNA Analysis
Once the DNA sample is collected, it is analyzed to identify specific genetic markers, known as alleles. These alleles are inherited from both parents and are unique to each individual, except in the case of identical twins.
- DNA Extraction:The first step in DNA analysis is to extract the DNA from the sample. This is done using a chemical process that breaks down the cells and releases the DNA.
- DNA Amplification:Once the DNA is extracted, it is amplified using a technique called PCR (polymerase chain reaction). PCR makes millions of copies of the specific DNA regions of interest.
- DNA Electrophoresis:The amplified DNA is then separated by size using a technique called electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are separated based on their size and electrical charge.
- DNA Visualization:The separated DNA fragments are visualized using a fluorescent dye. The pattern of the DNA fragments is unique to each individual and is used to create a DNA profile.
Gizmo Answer Key: Dna Profiling Gizmo Answer Key
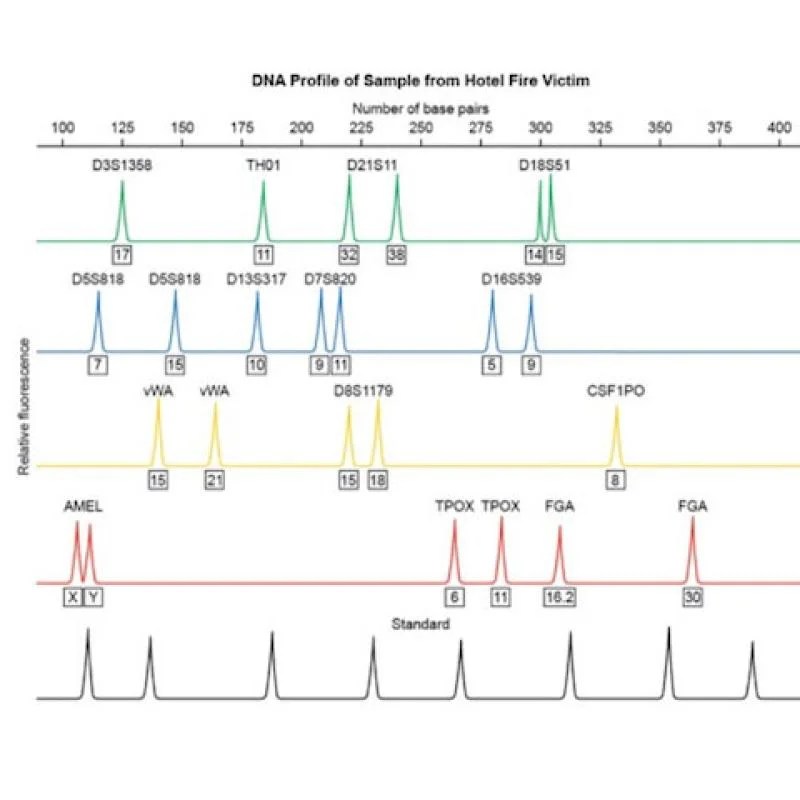
This comprehensive answer key provides detailed explanations for the Gizmo activity on DNA profiling. It covers key concepts such as DNA structure, gel electrophoresis, and DNA fingerprinting, ensuring a thorough understanding of the topic.
DNA Structure
- DNA is a double helix molecule composed of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- These bases pair specifically (A with T, C with G) to form base pairs, creating the iconic double helix structure.
- The sequence of base pairs along the DNA molecule carries genetic information.
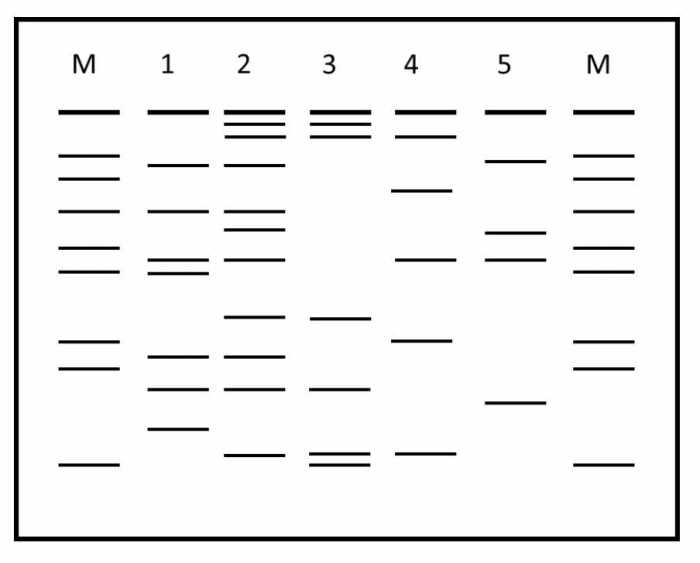
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments based on their size. Smaller fragments move faster through the gel, while larger fragments move slower.
- DNA fragments are loaded onto a gel and an electric current is applied.
- The negatively charged DNA fragments migrate towards the positive electrode.
- Smaller fragments move through the gel pores more easily than larger fragments, resulting in separation.
DNA Fingerprinting
DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profile. It involves analyzing specific regions of DNA that vary between individuals, known as variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs).
- VNTRs are short sequences of DNA that repeat a certain number of times.
- The number of repeats varies between individuals, creating unique DNA profiles.
- DNA fingerprinting is used in various applications, including forensic science, paternity testing, and genetic research.
Applications of DNA Profiling

DNA profiling has revolutionized various fields, including forensics, paternity testing, and medical diagnostics. Its ability to identify individuals based on their unique genetic makeup has led to numerous breakthroughs and advancements.
Forensic Applications
In forensics, DNA profiling has become an indispensable tool for solving crimes and identifying suspects. By comparing DNA samples from crime scenes to those of potential suspects or victims, investigators can determine if a particular individual was present at the scene or involved in the crime.
This technique has been successfully used to:
- Identify suspects in murder, rape, and assault cases
- Link multiple crimes to a single perpetrator
- Exonerate innocent individuals who were wrongly convicted
Paternity Testing
DNA profiling has also become a standard method for establishing paternity. By comparing the DNA of a child to that of the alleged father, paternity can be confirmed with almost 100% accuracy. This information is crucial for legal and personal reasons, such as:
- Establishing child support obligations
- Determining inheritance rights
- Providing peace of mind to individuals seeking to confirm their biological relationships
Medical Diagnostics
In the medical field, DNA profiling has opened up new possibilities for diagnosing genetic disorders and predicting an individual’s susceptibility to certain diseases. By analyzing an individual’s DNA, doctors can:
- Identify genetic mutations associated with specific disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease
- Determine the risk of developing inherited diseases, such as breast cancer and Alzheimer’s disease
- Develop personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s genetic makeup
Ethical Considerations
The use of DNA profiling raises several ethical concerns. These include privacy concerns, the use of DNA information in criminal justice, and the implications for genetic discrimination.
If you’re looking for the DNA Profiling Gizmo answer key, you might also be interested in knowing that nine thousandths as a decimal is 0.009 . The DNA Profiling Gizmo is a great tool for learning about DNA analysis, and it can be used to solve a variety of problems related to genetics and forensics.
Privacy Concerns
One of the main ethical concerns associated with DNA profiling is the potential for privacy violations. DNA contains a wealth of personal information, including information about an individual’s health, ancestry, and even personality traits. If this information is not properly protected, it could be used to discriminate against individuals or to invade their privacy.
Use of DNA Information in Criminal Justice
DNA profiling is a powerful tool for law enforcement. It can be used to identify suspects, convict criminals, and exonerate the innocent. However, there are also concerns about the potential for misuse of DNA information in criminal justice. For example, DNA profiling could be used to create a database of all Americans, which could be used to track people’s movements or to target them for discrimination.
Implications for Genetic Discrimination, Dna profiling gizmo answer key
Another ethical concern associated with DNA profiling is the potential for genetic discrimination. Genetic discrimination occurs when an individual is treated differently based on their genetic information. For example, an individual could be denied a job or insurance coverage based on their genetic predisposition to a particular disease.
Future Directions
DNA profiling technology is rapidly evolving, with advancements in DNA sequencing and data analysis opening up new possibilities. These advancements are paving the way for personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
One significant advancement is the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies, which allow for the rapid and cost-effective sequencing of large amounts of DNA. This has made it possible to sequence the entire human genome for a fraction of the cost of just a few years ago.
Another important advancement is the development of sophisticated data analysis tools that can identify patterns and associations in DNA sequences. These tools are essential for interpreting the vast amount of data generated by high-throughput sequencing.
Personalized Medicine
The combination of high-throughput sequencing and data analysis is making personalized medicine a reality. By understanding an individual’s unique genetic makeup, doctors can tailor treatments to their specific needs.
For example, DNA profiling can be used to identify individuals who are at risk for certain diseases, such as cancer or heart disease. This information can be used to develop preventive measures or to start treatment early, when it is most effective.
DNA profiling can also be used to predict how an individual will respond to certain medications. This information can help doctors choose the most effective treatment for each patient.
Personalized medicine is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat diseases.
Query Resolution
What is DNA profiling?
DNA profiling is a technique used to analyze DNA samples to identify individuals or determine genetic relationships.
How is DNA profiling used in forensics?
DNA profiling plays a crucial role in forensics, helping to identify suspects, exonerate the innocent, and solve crimes.
What are the ethical considerations associated with DNA profiling?
DNA profiling raises ethical concerns regarding privacy, potential misuse, and the implications for genetic discrimination.